As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication and scale, organizations must adopt proactive defense strategies to stay ahead of attackers. Honeypots, which have long been a valuable tool in the cybersecurity arsenal, are evolving to meet the challenges of the modern threat landscape. In 2025, deploying honeypots effectively requires a strategic approach that balances innovation, security, and operational efficiency.
In this blog, we’ll explore the best practices for deploying honeypots in 2025, covering everything from planning and implementation to monitoring and analysis. Whether you’re a seasoned security professional or new to the concept of honeypots, this guide will help you maximize their potential while minimizing risks.
Table of Contents
Why Honeypots Matter in 2025
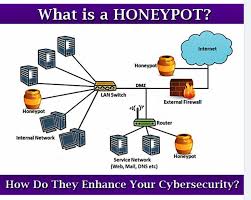
The cybersecurity landscape in 2025 is expected to be more complex than ever, with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the proliferation of IoT devices, and the rise of quantum computing reshaping the threat landscape. Honeypots will play a critical role in:
Detecting Advanced Threats: As attackers leverage AI and automation, honeypots can help identify novel attack techniques and zero-day exploits.
Gathering Threat Intelligence: Honeypots provide actionable insights into attacker behavior, tools, and tactics.
Enhancing Deception Strategies: Modern deception technologies rely on honeypots to mislead and confuse attackers.
Supporting Incident Response: Honeypots can serve as early warning systems, alerting organizations to potential breaches.
To harness the full potential of honeypots in 2025, organizations must follow best practices tailored to the evolving cybersecurity environment.
Best Practices for Deploying Honeypots in 2025
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before deploying a honeypot, it’s essential to define your goals. Ask yourself:
What type of threats are you trying to detect?
Are you focused on gathering threat intelligence, improving incident response, or testing your defenses?
What level of interaction do you need (low, medium, or high)?
Example: If your goal is to detect automated botnet activity, a low-interaction honeypot may suffice. For studying advanced persistent threats (APTs), a high-interaction honeypot or honeynet would be more appropriate.
2. Choose the Right Type of Honeypot
Honeypots come in various forms, each suited to specific use cases. In 2025, consider the following types:
Low-Interaction Honeypots: Ideal for detecting widespread, automated attacks.
High-Interaction Honeypots: Provide detailed insights into attacker behavior but require more resources.
Honeynets: Simulate entire networks to study coordinated attacks.
Honeytokens: Use fake data to detect unauthorized access or insider threats.
Pro Tip: In 2025, consider integrating AI-driven honeypots that can adapt to attacker behavior in real-time, making them more effective against sophisticated threats.
3. Isolate and Secure Your Honeypot
One of the biggest risks of deploying a honeypot is the potential for it to be used as a launchpad for attacks on your real systems. To mitigate this risk:
Segment Your Network: Place the honeypot in a isolated network segment, separate from critical systems.
Use Virtualization: Deploy honeypots in virtual environments to limit their impact if compromised.
Implement Access Controls: Restrict access to the honeypot to authorized personnel only.
Example: Use a demilitarized zone (DMZ) or a dedicated virtual LAN (VLAN) for your honeypot deployment.
4. Leverage Automation and AI
In 2025, automation and AI will be essential for managing honeypots at scale. Consider the following:
Automated Deployment: Use tools like Docker or Kubernetes to deploy and manage honeypots dynamically.
AI-Powered Analysis: Leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze attacker behavior and identify patterns.
Adaptive Honeypots: Deploy honeypots that can change their behavior based on the attacker’s actions, making them harder to detect.
Pro Tip: Integrate your honeypot with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system to automate threat detection and response.
5. Ensure Realistic Simulation
To effectively lure attackers, your honeypot must appear authentic. This includes:
Mimicking Real Systems: Simulate real operating systems, applications, and services.
Using Fake Data: Populate the honeypot with realistic but fake data to make it more enticing.
Avoiding Obvious Traps: Ensure the honeypot doesn’t have easily detectable signs of being a trap, such as default configurations or unrealistic vulnerabilities.
Example: If simulating a web server, include fake login pages, user accounts, and database entries.
6. Monitor and Analyze Activity
The value of a honeypot lies in the data it collects. To maximize its effectiveness:
Log All Activity: Capture detailed logs of all interactions with the honeypot, including IP addresses, timestamps, and commands executed.
Use Behavioral Analytics: Analyze attacker behavior to identify trends and anomalies.
Share Threat Intelligence: Contribute anonymized data to threat intelligence platforms to help the broader cybersecurity community.
Pro Tip: In 2025, consider using blockchain technology to securely store and share honeypot data, ensuring its integrity and authenticity.
7. Stay Compliant with Legal and Ethical Guidelines
Deploying honeypots raises legal and ethical considerations, such as:
Privacy Concerns: Ensure your honeypot does not inadvertently capture sensitive data from legitimate users.
Entrapment Risks: Avoid practices that could be construed as entrapment, which may have legal implications.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure your honeypot deployment complies with relevant laws and regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
Example: Consult with legal experts to ensure your honeypot deployment aligns with local and international laws.
8. Regularly Update and Maintain Your Honeypot
Honeypots require ongoing maintenance to remain effective. Best practices include:
Patching Vulnerabilities: Regularly update the software and services running on the honeypot to prevent it from being exploited.
Rotating Configurations: Change the honeypot’s configuration periodically to keep attackers guessing.
Reviewing Logs: Continuously analyze logs to identify new threats and adjust your defenses accordingly.
Pro Tip: In 2025, consider using containerized honeypots that can be easily updated and replaced without disrupting operations.
9. Integrate with Broader Security Strategies
Honeypots should not operate in isolation. Integrate them with your overall security strategy by:
Feeding Data to SIEMs: Use honeypot data to enrich threat intelligence and improve detection capabilities.
Collaborating with Incident Response Teams: Ensure your incident response team is prepared to act on insights gathered from the honeypot.
Combining with Deception Technologies: Use honeypots as part of a broader deception strategy to confuse and mislead attackers.
Example: Deploy honeypots alongside intrusion detection systems (IDS) and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions for a layered defense.
10. Educate and Train Your Team
Finally, ensure your team is equipped to deploy and manage honeypots effectively. This includes:
Providing Training: Educate your team on honeypot deployment, monitoring, and analysis.
Conducting Simulations: Use honeypots in training exercises to simulate real-world attack scenarios.
Staying Informed: Keep up with the latest trends and advancements in honeypot technology.
Pro Tip: In 2025, consider partnering with cybersecurity vendors or joining industry forums to stay updated on best practices and emerging threats.
Conclusion
Deploying honeypots in 2025 requires a strategic and forward-thinking approach. By following these best practices, organizations can leverage honeypots to detect advanced threats, gather actionable intelligence, and enhance their overall security posture. As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, honeypots will remain a critical tool for staying one step ahead of attackers.
Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, now is the time to invest in honeypot technology and integrate it into your cybersecurity strategy. By doing so, you’ll be better prepared to face the challenges of 2025 and beyond.
Also Read on: Deploying Honeypots in Cloud Environments
Why Businesses Trust SecureMyOrg for Comprehensive Network Security
At SecureMyOrg, we uncover and fix all possible security vulnerabilities of mobile and web, while providing solutions to mitigate risks. We are trusted by renowned companies like Yahoo, Gojek and Rippling, and with 100% client satisfaction, you’re in safe hands!







Some of the things people reach out to us for –
- Building their cybersecurity program from scratch – setting up cloud security using cost-effective tools, SIEM for alert monitoring, building policies for the company
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing ( VAPT ) – We have certified professionals, with certifications like OSCP, CREST – CPSA & CRT, CKA and CKS
- DevSecOps consulting
- Red Teaming activity
- Regular security audits, before product release
- Full time security engineers.
Relevant Posts

Top Cybersecurity Threats Facing Businesses In 2026
Businesses entering 2026 face a security landscape that is more complex, more interconnected, and far less forgiving than in previous years. Cybersecurity threats no longer

Top 5 Security Weaknesses Cloud-Native Apps Commonly Ignore
Cloud-native applications promise speed, flexibility, and scalability. Teams ship features faster, infrastructure adapts automatically, and operational overhead drops. Yet many organizations discover later that security

Why Weak Serverless Application Security Puts Your Business at Risk
Weak security in serverless environments often goes unnoticed until it leads to real damage. Misconfigured triggers, broad permissions, and poor visibility can expose sensitive data and disrupt business operations. Understanding where the risks appear is the first step toward building safer, more reliable serverless applications.

What Is Penetration Testing as a Service?
Penetration testing as a service (PTaaS) lets experts simulate real attacks to uncover vulnerabilities before hackers do. This guide explains the process, benefits, and costs, helping businesses strengthen defenses with predictable, ongoing security checks.

How To Inspect Encrypted Traffic Without Breaking Privacy
Network administrators face a challenge: securing systems while respecting privacy. This guide explains how to inspect encrypted traffic without breaking privacy using metadata, anomaly detection, and machine learning ensuring visibility, compliance, and trust.

How to Audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Security Vulnerabilities
Discover how to audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for security vulnerabilities with this practical guide. Learn to scan IaC files using tools like Checkov, fix issues like exposed resources, and integrate audits into CI/CD pipelines. Protect your cloud systems from misconfigurations and ensure compliance with clear, actionable steps.

