Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks are one of the most disruptive cyber threats today. These attacks overwhelm a network, server, or application with excessive traffic, rendering services inaccessible to legitimate users. Hackers use various methods to execute DDoS attacks, each targeting different network layers and exploiting specific vulnerabilities.
In this article, we’ll break down the major types of DDoS attacks, their mechanisms, and how they impact online services. We will also delve into Layer 7 DDoS attacks, a particularly sophisticated type that targets the application layer.
Table of Contents
The Types of DDoS Attacks

A DDoS attack can be classified into three main types:
Volumetric Attacks – These flood the target with massive amounts of traffic, exhausting bandwidth. Examples include UDP Floods, ICMP Floods, and DNS Amplification.
Protocol Attacks – These exploit weaknesses in network protocols to consume server resources. Examples include SYN Floods, Ping of Death, and Smurf Attacks.
Application-Layer Attacks – These target specific applications, exhausting resources at the application level. Examples include HTTP Floods and Slowloris attacks.
The Multi-Vector DDoS attack is a further classification of the types of DDoS attacks. We look into some examples and impacts of the listed types DDoS attacks and possible procedures for mitigation.
1. Volumetric DDoS Attacks
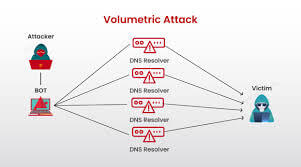
-volumetric attacks: Image from infosec blog
Volumetric attacks are the most common form of DDoS attacks. They flood the target with massive amounts of data or requests, consuming all available bandwidth and preventing legitimate traffic from reaching the system.
Common Volumetric Attacks:
- UDP Floods – Send large amounts of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets to random ports, forcing the target system to respond with “destination unreachable” messages.
- ICMP Floods (Ping Floods) – Bombard a network with ICMP (ping) requests, exhausting bandwidth and processing capacity.
- DNS Amplification – Exploits vulnerable DNS servers by sending small requests with spoofed IP addresses that trigger large responses, overwhelming the target.
- NTP Amplification – Uses Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers to amplify attack traffic, similar to DNS amplification.
Impact:
Volumetric DDoS attacks can cause massive internet slowdowns or complete service outages, affecting businesses, government services, and online platforms.
2. Protocol-Based DDoS Attacks
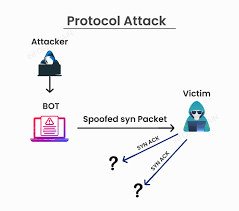
-protocol attack: Images from infosec blog
These attacks exploit weaknesses in network protocols to consume server resources or disrupt network connections.
Common Protocol-Based Attacks:
- SYN Floods – Exploit the TCP handshake process by sending a large number of SYN requests without completing the handshake, exhausting server resources.
- ACK Floods – Overload a target by sending a flood of TCP ACK packets, forcing the server to allocate resources for processing these fake acknowledgments.
- Smurf Attack – Uses ICMP requests with a spoofed IP address to flood a victim with echo replies from multiple devices.
- Ping of Death – Sends oversized or malformed ping packets that crash the target system.
Impact:
These attacks do not necessarily consume large amounts of bandwidth but can paralyze a server by exhausting its processing capacity.
3. Application-Layer (Layer 7) DDoS Attacks
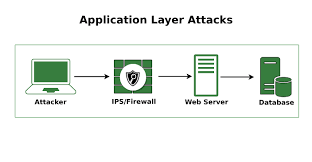
-Application Layer Attack: Images from geeks-for-geeks
Unlike volumetric or protocol-based attacks, Layer 7 DDoS attacks target the application layer (OSI Layer 7), where websites and online services process user requests. These attacks are harder to detect because they mimic normal user behavior, making traditional mitigation techniques less effective.
How Layer 7 DDoS Attacks Work:
- Attackers send seemingly legitimate HTTP requests to web servers, overloading them with excessive processing tasks.
- These requests often target resource-intensive actions, such as database queries, login authentication, or dynamic page rendering.
- Since the traffic looks like real user activity, traditional firewalls and rate-limiting mechanisms struggle to block it.
Common Layer 7 DDoS Attacks:
- HTTP Floods – Attackers continuously send HTTP GET or POST requests, causing the web server to use all its resources.
- Slowloris Attack – A slow but persistent attack where an attacker holds connections open for extended periods by sending partial HTTP requests, preventing the server from serving other users.
- DNS Query Floods – Overload DNS servers by sending a high volume of DNS requests, leading to service unavailability.
- Botnet-Based Attacks – Large-scale botnets, often made up of compromised IoT devices, send overwhelming traffic to applications, making them unresponsive.
Impact:
Layer 7 DDoS attacks can bring down e-commerce platforms, APIs, and content delivery networks (CDNs) by exhausting web server resources. Unlike volumetric attacks, they require fewer packets but cause significant damage by targeting server-side processing power.
4. Multi-Vector DDoS Attacks
Many modern DDoS attacks combine multiple attack types, making them more challenging to mitigate. Multi-vector attacks use a combination of volumetric, protocol-based, and application-layer methods, increasing the complexity of defense strategies.
Example of a Multi-Vector Attack:
- A hacker launches a UDP flood (volumetric) to clog the network.
- Simultaneously, a SYN flood (protocol-based) is initiated to exhaust server resources.
- Finally, an HTTP flood (Layer 7 attack) overwhelms the web application, making it impossible for users to log in or access services.
Impact:
Multi-vector attacks are difficult to stop because they require a layered defense strategy that includes traffic analysis, deep packet inspection, and advanced AI-based security solutions.
How to Mitigate DDoS Attacks
Preventing and mitigating DDoS attacks requires a multi-layered approach:
- Deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Helps filter and block malicious Layer 7 traffic.
- Use Rate Limiting: Restricts the number of requests from a single IP address.
- Enable DDoS Protection Services: Cloud-based services like Cloudflare, Akamai, and AWS Shield provide real-time traffic filtering.
- Implement Network Traffic Analysis: Identifies abnormal traffic patterns using AI-powered solutions.
- Use Anycast Networks: Distributes traffic across multiple data centers to absorb large-scale attacks.
- Strengthen DNS Security: Prevents DNS-based amplification attacks.
- Monitor for Anomalous Activity: Early detection helps stop attacks before they escalate.
Conclusion
DDoS attacks are evolving, becoming more sophisticated and harder to detect. Understanding the different types of DDoS attacks—volumetric, protocol-based, and application-layer attacks—helps businesses prepare and deploy effective mitigation strategies.
Among these, Layer 7 DDoS attacks pose a unique challenge, as they target the application layer where legitimate user traffic resides. Advanced security measures, AI-powered monitoring, and cloud-based defenses are essential to combating these threats.
By staying proactive and implementing robust security defenses, organizations can minimize the impact of DDoS attacks and ensure uninterrupted services for users.
Why Businesses Trust SecureMyOrg For Comprehensive Network Security
At SecureMyOrg, we uncover and fix all possible security vulnerabilities of mobile and web, while providing solutions to mitigate risks. We are trusted by renowned companies like Yahoo, Gojek and Rippling, and with 100% client satisfaction, you’re in safe hands!







Some of the things people reach out to us for –
- Building their cybersecurity program from scratch – setting up cloud security using cost-effective tools, SIEM for alert monitoring, building policies for the company
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing ( VAPT ) – We have certified professionals, with certifications like OSCP, CREST – CPSA & CRT, CKA and CKS
- DevSecOps consulting
- Red Teaming activity
- Regular security audits, before product release
- Full time security engineers.
Relevant Posts

Top Cybersecurity Threats Facing Businesses In 2026
Businesses entering 2026 face a security landscape that is more complex, more interconnected, and far less forgiving than in previous years. Cybersecurity threats no longer

Top 5 Security Weaknesses Cloud-Native Apps Commonly Ignore
Cloud-native applications promise speed, flexibility, and scalability. Teams ship features faster, infrastructure adapts automatically, and operational overhead drops. Yet many organizations discover later that security

Why Weak Serverless Application Security Puts Your Business at Risk
Weak security in serverless environments often goes unnoticed until it leads to real damage. Misconfigured triggers, broad permissions, and poor visibility can expose sensitive data and disrupt business operations. Understanding where the risks appear is the first step toward building safer, more reliable serverless applications.

What Is Penetration Testing as a Service?
Penetration testing as a service (PTaaS) lets experts simulate real attacks to uncover vulnerabilities before hackers do. This guide explains the process, benefits, and costs, helping businesses strengthen defenses with predictable, ongoing security checks.

How To Inspect Encrypted Traffic Without Breaking Privacy
Network administrators face a challenge: securing systems while respecting privacy. This guide explains how to inspect encrypted traffic without breaking privacy using metadata, anomaly detection, and machine learning ensuring visibility, compliance, and trust.

How to Audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Security Vulnerabilities
Discover how to audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for security vulnerabilities with this practical guide. Learn to scan IaC files using tools like Checkov, fix issues like exposed resources, and integrate audits into CI/CD pipelines. Protect your cloud systems from misconfigurations and ensure compliance with clear, actionable steps.
