In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, defenders are constantly seeking innovative ways to outsmart attackers. One such tool that has gained significant attention is the honeypot. But what exactly is a honeypot, and how does it work? In this blog, we’ll dive into the concept of honeypots, explore how they function, and discuss their benefits, types, and real-world applications in cybersecurity.
What is a Honeypot?
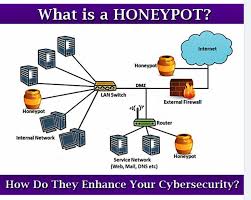
Honeypots in Cybersecurity -image by teleforum
A honeypot is a security mechanism designed to mimic a real system, network, or application to attract and deceive cyber attackers. Think of it as a digital “trap” that lures malicious actors into interacting with it, allowing security professionals to study their behavior, gather intelligence, and improve defenses.
Unlike traditional security tools that focus on blocking attacks, honeypots are proactive. They intentionally expose vulnerabilities to entice attackers, making them a valuable tool for understanding threat landscapes and identifying emerging attack techniques.

-Book Your Free Security Consultation Now!
Table of Contents
How Does a Honeypot Work?
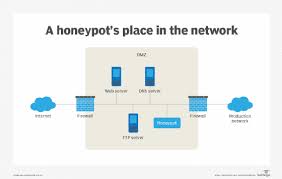
At its core, a honeypot works by simulating a legitimate target. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it operates:
1. Deployment
A honeypot is set up to resemble a real system, such as a server, database, or IoT device. It is often placed in a network segment that is isolated from critical systems to prevent any potential damage.
2. Attraction
The honeypot is designed to appear vulnerable or enticing to attackers. For example, it might simulate an unpatched server or a database containing fake sensitive information. Attackers are drawn to these seemingly easy targets.
3. Interaction
Once an attacker interacts with the honeypot, their actions are closely monitored. This includes tracking the tools they use, the commands they execute, and the techniques they employ to exploit the system.
4. Data Collection
The honeypot collects valuable data about the attacker’s behavior, such as IP addresses, malware samples, and attack patterns. This information is then analyzed to gain insights into the threat landscape.
5. Analysis and Response
Security teams use the data gathered from the honeypot to improve their defenses. For example, they might identify new attack vectors, update intrusion detection systems, or patch vulnerabilities in real systems.
Types of Honeypots
Honeypots come in various forms, each tailored to specific use cases and levels of interaction. Here are the main types:
1. Low-Interaction Honeypots
These honeypots simulate only the most basic services and protocols. They are easy to deploy and maintain but provide limited information about attacker behavior. Examples include honeypots that mimic a simple web server or FTP service.
Use Case: Ideal for detecting widespread, automated attacks like botnets or script-based exploits.
2. High-Interaction Honeypots
High-interaction honeypots simulate full systems or networks, allowing attackers to interact with them as they would with a real target. These honeypots provide detailed insights into attacker behavior but require more resources and carry higher risks.
Use Case: Suitable for researching advanced threats and studying the tactics of skilled attackers.
3. Pure Honeypots
These are fully functional systems that mimic real production environments. They are complex to set up and manage but offer the most realistic interaction for attackers.
Use Case: Used in high-security environments to gather in-depth intelligence on targeted attacks.
4. Honeynets
A honeynet is a network of honeypots designed to simulate an entire network infrastructure. It provides a broader view of attacker behavior and is often used to study coordinated attacks.
Use Case: Effective for analyzing large-scale attacks and understanding how attackers move laterally within a network.
5. Honeytokens
While not a traditional honeypot, honeytokens are fake data or credentials planted within a system to detect unauthorized access. For example, a fake database entry or API key can act as a honeytoken.
Use Case: Useful for detecting insider threats or data breaches.
Benefits of Using Honeypots
Honeypots offer several advantages in the realm of cybersecurity:
1. Threat Intelligence
Honeypots provide firsthand insights into attacker behavior, tools, and techniques. This information is invaluable for improving defenses and staying ahead of emerging threats.
2. Reduced False Positives
Unlike traditional security tools that generate numerous alerts, honeypots only log activity when an attacker interacts with them. This reduces noise and allows security teams to focus on real threats.
3. Cost-Effective
Honeypots are relatively inexpensive to deploy and maintain, especially when compared to other security solutions like intrusion detection systems (IDS) or firewalls.
4. Proactive Defense
By luring attackers into a controlled environment, honeypots enable organizations to study and mitigate threats before they can cause harm to real systems.
5. Compliance and Forensics
Honeypots can help organizations meet regulatory requirements by providing detailed logs of attack attempts. They also serve as valuable tools for forensic investigations.
Challenges and Risks of Honeypots
While honeypots are powerful tools, they are not without challenges:
1. Risk of Compromise
If not properly isolated, a honeypot can be used as a launchpad for attacks on real systems. Proper segmentation and monitoring are essential to mitigate this risk.
2. Limited Scope
Honeypots only capture activity directed at them, meaning they won’t detect attacks targeting other parts of the network.
3. Resource Intensive
High-interaction honeypots and honeynets require significant resources to set up and maintain, making them less feasible for smaller organizations.
4. Ethical and Legal Concerns
Deploying honeypots raises ethical and legal questions, such as the potential for entrapment or violations of privacy laws. Organizations must ensure their use of honeypots complies with relevant regulations.
Real-World Applications of Honeypots
Honeypots are used in a variety of scenarios to enhance cybersecurity:
1. Threat Research
Security researchers use honeypots to study new malware, zero-day exploits, and attack techniques. For example, honeypots have been instrumental in analyzing ransomware campaigns and botnet activities.
2. Incident Response
Honeypots can serve as early warning systems, alerting organizations to potential breaches and providing valuable data for incident response teams.
3. Education and Training
Honeypots are often used in cybersecurity training programs to simulate real-world attack scenarios and help students develop hands-on skills.
4. Deception Technology
Modern deception platforms leverage honeypots to create a network of decoys that confuse and mislead attackers, buying time for defenders to respond.
Conclusion
Honeypots are a fascinating and powerful tool in the cybersecurity arsenal. By luring attackers into a controlled environment, they provide invaluable insights into threat landscapes and help organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. While they come with their own set of challenges, the benefits of using honeypots far outweigh the risks when implemented correctly.
Whether you’re a security professional looking to enhance your defenses or a researcher seeking to understand emerging threats, honeypots offer a unique and proactive approach to cybersecurity. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, honeypots will undoubtedly remain a critical tool in the fight against cybercrime.
References
Why Businesses Trust SecureMyOrg for Comprehensive Network Security
At SecureMyOrg, we uncover and fix all possible security vulnerabilities of mobile and web, while providing solutions to mitigate risks. We are trusted by renowned companies like Yahoo, Gojek and Rippling, and with 100% client satisfaction, you’re in safe hands!







Some of the things people reach out to us for –
- Building their cybersecurity program from scratch – setting up cloud security using cost-effective tools, SIEM for alert monitoring, building policies for the company
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing ( VAPT ) – We have certified professionals, with certifications like OSCP, CREST – CPSA & CRT, CKA and CKS
- DevSecOps consulting
- Red Teaming activity
- Regular security audits, before product release
- Full time security engineers.
Relevant Posts

Top Cybersecurity Threats Facing Businesses In 2026
Businesses entering 2026 face a security landscape that is more complex, more interconnected, and far less forgiving than in previous years. Cybersecurity threats no longer

Top 5 Security Weaknesses Cloud-Native Apps Commonly Ignore
Cloud-native applications promise speed, flexibility, and scalability. Teams ship features faster, infrastructure adapts automatically, and operational overhead drops. Yet many organizations discover later that security

Why Weak Serverless Application Security Puts Your Business at Risk
Weak security in serverless environments often goes unnoticed until it leads to real damage. Misconfigured triggers, broad permissions, and poor visibility can expose sensitive data and disrupt business operations. Understanding where the risks appear is the first step toward building safer, more reliable serverless applications.

What Is Penetration Testing as a Service?
Penetration testing as a service (PTaaS) lets experts simulate real attacks to uncover vulnerabilities before hackers do. This guide explains the process, benefits, and costs, helping businesses strengthen defenses with predictable, ongoing security checks.

How To Inspect Encrypted Traffic Without Breaking Privacy
Network administrators face a challenge: securing systems while respecting privacy. This guide explains how to inspect encrypted traffic without breaking privacy using metadata, anomaly detection, and machine learning ensuring visibility, compliance, and trust.

How to Audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Security Vulnerabilities
Discover how to audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for security vulnerabilities with this practical guide. Learn to scan IaC files using tools like Checkov, fix issues like exposed resources, and integrate audits into CI/CD pipelines. Protect your cloud systems from misconfigurations and ensure compliance with clear, actionable steps.
