Cybersecurity threats are evolving, attackers are getting more creative. Among the most insidious of these threats is the Remote Access Trojan (RAT), a type of malware that allows attackers to secretly control a victim’s computer or device. Unlike traditional viruses or worms, RATs are designed to operate stealthily, giving cybercriminals unrestricted access to sensitive data, systems, and networks. But what exactly is a RAT, how does it work, and why is it such a significant threat? In this blog, we’ll break down the concept of RATs, explore how they differ from legitimate remote access tools, and discuss the risks they pose—along with real-world examples and tips for prevention.
What is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT)?
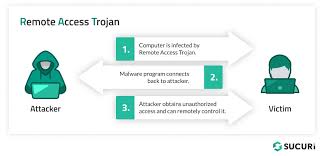
A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) is a type of malicious software that provides an attacker with unauthorized remote control over a victim’s computer or device. Once installed, a RAT allows the attacker to perform a wide range of activities, such as stealing sensitive data, monitoring user activity, executing commands, and even spreading malware to other systems. The term “Trojan” comes from the ancient Greek story of the Trojan Horse, where soldiers hid inside a seemingly harmless gift to infiltrate a city. Similarly, a RAT disguises itself as legitimate software or hides within another file to trick users into installing it.
RATs are particularly dangerous because they operate covertly, often without the victim’s knowledge. Unlike ransomware, which announces its presence by encrypting files and demanding payment, a RAT works silently in the background, giving attackers prolonged access to the infected system.
How Do RATs Differ from Legitimate Remote Access Tools?
At first glance, RATs may seem similar to legitimate remote access tools like TeamViewer, AnyDesk, or Microsoft Remote Desktop. These tools are designed to allow users to remotely control computers for legitimate purposes, such as providing technical support or accessing files from another location. However, there are key differences between legitimate tools and RATs:
Intent and Authorization:
Legitimate remote access tools are used with the explicit consent of the device owner. In contrast, RATs are installed without the user’s knowledge or permission, often through deceptive means.Stealth and Malicious Functionality:
RATs are designed to evade detection by antivirus software and operate in the background. They often include additional malicious features, such as keylogging, screen capturing, and data exfiltration.Distribution Methods:
Legitimate tools are downloaded from official sources, while RATs are typically distributed through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or compromised websites.Purpose:
Legitimate tools are used for productivity and support, whereas RATs are used for malicious activities like espionage, data theft, and system sabotage.
Common Methods Attackers Use to Deliver RATs

-Attackers can use phishing emails to deliver Remote Access Trojans
Cybercriminals use a variety of tactics to deliver RATs to their victims. Some of the most common methods include:
Phishing Emails:
Attackers send emails disguised as legitimate messages, often containing malicious attachments or links. When the victim opens the attachment or clicks the link, the RAT is installed on their system.Malicious Downloads:
RATs can be hidden in pirated software, games, or other downloadable files. Users who download and install these files unknowingly infect their devices.Exploiting Vulnerabilities:
Attackers exploit security vulnerabilities in software or operating systems to deliver RATs without user interaction.Social Engineering:
Cybercriminals use psychological manipulation to trick users into installing RATs. For example, they might pose as tech support and convince the victim to download a “necessary update” that is actually a RAT.Drive-By Downloads:
Simply visiting a compromised or malicious website can result in the automatic download and installation of a RAT.
The Risks and Potential Damage Caused by RATs
The consequences of a RAT infection can be severe, both for individuals and organizations. Here are some of the key risks:
Data Theft:
RATs can steal sensitive information, including passwords, financial data, and personal files. This information can be used for identity theft, fraud, or sold on the dark web.Espionage:
Attackers can use RATs to spy on victims by capturing screenshots, recording keystrokes, or even activating webcams and microphones.System Manipulation:
RATs allow attackers to execute commands on the infected system, such as deleting files, installing additional malware, or disrupting operations.Network Propagation:
Once inside a network, RATs can spread to other devices, creating a larger attack surface and increasing the potential damage.Financial Loss:
For businesses, a RAT infection can lead to significant financial losses due to data breaches, operational downtime, and reputational damage.Long-Term Access:
RATs are designed to remain undetected for long periods, giving attackers prolonged access to the victim’s system and data.
Real-World Examples of RAT Attacks
To understand the real-world impact of RATs, let’s look at a few notable examples:
DarkComet:
DarkComet was a widely used RAT that gained notoriety during the Syrian civil war. It was used to spy on activists by capturing screenshots, logging keystrokes, and activating webcams. The RAT was distributed through phishing emails and malicious links.NjRat:
NjRat is a RAT that has been used extensively in the Middle East and North Africa. It allows attackers to steal data, execute commands, and even disable antivirus software. NjRat is often distributed through malicious USB drives and fake software updates.PoisonIvy:
PoisonIvy is a RAT that was used in a series of high-profile cyber espionage campaigns, including attacks on defense contractors and government agencies. The RAT was delivered through spear-phishing emails and exploited vulnerabilities in software like Adobe Reader.
How to Protect Against RATs
Preventing RAT infections requires a combination of technical measures and user awareness. Here are some key steps to protect yourself or your organization:
Use Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software:
Regularly update and run antivirus software to detect and remove RATs.Keep Software Updated:
Install security patches for your operating system and software to close vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.Be Cautious with Emails and Downloads:
Avoid opening attachments or clicking links in unsolicited emails. Only download software from trusted sources.Enable Firewalls:
Use firewalls to block unauthorized access to your network.Educate Users:
Train employees and family members to recognize phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics.Monitor Network Activity:
Regularly monitor network traffic for unusual activity that could indicate a RAT infection.Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication:
Protect your accounts with strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication where possible.
Conclusion
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are a significant and evolving threat in the cybersecurity landscape. By understanding how they function, how they differ from legitimate tools, and the risks they pose, individuals and organizations can take proactive steps to protect themselves. Real-world examples like DarkComet, NjRat, and PoisonIvy highlight the devastating impact of RAT attacks, underscoring the importance of awareness and prevention. By staying vigilant and implementing robust security measures, you can reduce the risk of falling victim to this invisible threat and safeguard your digital life.
References
Why Businesses Trust SecureMyOrg for Comprehensive Network Security
At SecureMyOrg, we uncover and fix all possible security vulnerabilities of mobile and web, while providing solutions to mitigate risks. We are trusted by renowned companies like Yahoo, Gojek and Rippling, and with 100% client satisfaction, you’re in safe hands!







Some of the things people reach out to us for –
- Building their cybersecurity program from scratch – setting up cloud security using cost-effective tools, SIEM for alert monitoring, building policies for the company
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing ( VAPT ) – We have certified professionals, with certifications like OSCP, CREST – CPSA & CRT, CKA and CKS
- DevSecOps consulting
- Red Teaming activity
- Regular security audits, before product release
- Full time security engineers.
Relevant Posts

Top Cybersecurity Threats Facing Businesses In 2026
Businesses entering 2026 face a security landscape that is more complex, more interconnected, and far less forgiving than in previous years. Cybersecurity threats no longer

Top 5 Security Weaknesses Cloud-Native Apps Commonly Ignore
Cloud-native applications promise speed, flexibility, and scalability. Teams ship features faster, infrastructure adapts automatically, and operational overhead drops. Yet many organizations discover later that security

Why Weak Serverless Application Security Puts Your Business at Risk
Weak security in serverless environments often goes unnoticed until it leads to real damage. Misconfigured triggers, broad permissions, and poor visibility can expose sensitive data and disrupt business operations. Understanding where the risks appear is the first step toward building safer, more reliable serverless applications.

What Is Penetration Testing as a Service?
Penetration testing as a service (PTaaS) lets experts simulate real attacks to uncover vulnerabilities before hackers do. This guide explains the process, benefits, and costs, helping businesses strengthen defenses with predictable, ongoing security checks.

How To Inspect Encrypted Traffic Without Breaking Privacy
Network administrators face a challenge: securing systems while respecting privacy. This guide explains how to inspect encrypted traffic without breaking privacy using metadata, anomaly detection, and machine learning ensuring visibility, compliance, and trust.

How to Audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for Security Vulnerabilities
Discover how to audit Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for security vulnerabilities with this practical guide. Learn to scan IaC files using tools like Checkov, fix issues like exposed resources, and integrate audits into CI/CD pipelines. Protect your cloud systems from misconfigurations and ensure compliance with clear, actionable steps.